Vocabularies — view dictionary terms
DIC_ROCK_ALL (3677 rows)
Dictionary table based on the entire version 3 of the BGS Rock Classification Scheme and is populated directly from the 3 supplying tables (BGS.ROCK_NAME_V3, BGS.ROCK_COMPOSITE and BGS.DIC_ROCK_DUMMY). It contains both the base rock names and addditional codes required for specific application, eg. composite names for use on digital geological maps. It is formally approved as the official source of ALL database codes to be used in BGS corporate databases and MUST be followed.

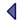 Displaying rows 2458 to 2477 of 3677
Displaying rows 2458 to 2477 of 3677


| Row | CODE | SOURCE_CODE | DESCRIPTION | TRANSLATION | STATUS | USER_ENTERED | DATE_ENTERED | USER_UPDATED | DATE_UPDATED | TRANSFER | RCS_STATUS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2458 | MYLH | RN | Mylonite, hornfelsed | Hornfelsed mylonite | C | AWEL | 21-SEP-01 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | U | |
| 2459 | MYLO | RN | Mylonite - A type of mylonitic-rock. In the Rock Classification Scheme, it is one in which porphyroclasts comprise 10 - 50% by volume of the rock. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/02, section 7.3 and table 5. | Mylonite | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 22-FEB-19 | R | |
| 2460 | MYLQ | RN | Mylonite, quartzose | Quartzose mylonite | C | AWEL | 13-MAR-01 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | U | |
| 2461 | MYLTIC | RN | Mylonitic-rock - A type of foliated mechanically broken rock with primary cohesion. Mylonitic rocks represent the products of dominantly ductile deformation. They generally occur within restricted zones related to faults, thrusts or shear zones. These foliated rocks develop as a result of grain size reduction by a combination of breakage and plastic strain of grains. Plastic deformation increases the aspect ratio of affected minerals producing textures such as quartz ribbons and a foliated fine-grained matrix. Other minerals, for example feldspar and garnet, may resist ductile deformation or fracture in a brittle manner and remain significantly larger than the foliated matrix. These are commonly lens shaped and termed porphyroclasts. As mylonitisation proceeds, the porphyroclasts are progressively wrapped by and then become isolated within the foliated matrix. They also become smaller, either by fracturing or by marginal erosion. Porphyroclasts may develop asymmetrical tails which can indicate the sense of shearing (dextral or sinistral) within the mylonitic rocks. Mylonitic rocks are classified into protomylonite, mylonite, and ultramylonite based on the percentage of visible porphyroclasts within the streaky, platy, fine-grained matrix. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/02, section 7.3 and table 5. | Mylonitic-rock | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 22-FEB-19 | R | |
| 2462 | MZ | RN | Monzonite - A type of syenitic-rock. In the Rock Classification Scheme, it is a coarse-grained crystalline igneous rock whose mineral mode plots in field 8 of the quartz - alkali feldspar - plagioclase - feldspathoid (QAPF) diagram. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/06, section 5.1 and figs. 9, 11, 12. | Monzonite | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 22-FEB-19 | R | |
| 2463 | MZCH | RN | Monzonite, charnockitic | Charnockitic monzonite | C | AWEL | 17-DEC-04 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | I | U |
| 2464 | MZDI | RN | Monzodiorite - A type of dioritic-rock. In the Rock Classification Scheme, it is a coarse-grained crystalline igneous rock whose mineral mode plots in field 9 of the quartz - alkali feldspar - plagioclase - feldspathoid (QAPF) diagram. Monzodiorite and monzogabbro are separated according to the average composition of their plagioclase: if An (the anorthite content of plagioclase) is less than 50% the rock is monzodiorite. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/06, section 5.1 and figs. 9, 11, 12. | Monzodiorite | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 22-FEB-19 | R | |
| 2465 | MZDIO | RN | Monzodiorite, olivine | Olivine monzodiorite | C | AWEL | 15-FEB-01 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | U | |
| 2466 | MZDO | RC | Olivine monzonite and olivine monzodiorite | Olivine monzonite and olivine monzodiorite | C | DJLO | 05-JUN-06 | TMCM | 24-AUG-18 | I | ? |
| 2467 | MZFO | RN | Monzonite, foliated | Foliated monzonite | C | AWEL | 27-MAR-01 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | U | |
| 2468 | MZGAB | RN | Monzogabbro - A type of gabbroic-rock. In the Rock Classification Scheme, it is a coarse-grained crystalline igneous rock whose mineral mode plots in field 9 of the quartz - alkali feldspar - plagioclase - feldspathoid (QAPF) diagram. Monzodiorite and monzogabbro are separated according to the average composition of their plagioclase: if An (the anorthite content of plagioclase) is greater than 50% the rock is monzogabbro. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/06, section 5.1 and figs. 9, 11, 12. | Monzogabbro | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 22-FEB-19 | R | |
| 2469 | MZGN | RN | Monzogranite - A type of granite. In the Rock Classification Scheme, it is a coarse-grained crystalline igneous rock whose mineral mode plots in field 3b of the quartz - alkali feldspar - plagioclase - feldspathoid (QAPF) diagram. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/06, section 5.1 and figs. 9, 11, 12. | Monzogranite | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 22-FEB-19 | R | |
| 2470 | MZGNB | RN | Monzogranite, biotite | Biotite monzogranite | C | AWEL | 15-FEB-01 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | U | |
| 2471 | MZGNL | RN | Leucomonzogranite | Leucomonzogranite | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | N | |
| 2472 | MZGP | RN | Monzogranite, porphyritic | Porphyritic monzogranite | C | AWEL | 13-FEB-01 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | U | |
| 2473 | MZOL | RN | Monzonite, olivine | Olivine monzonite | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | U | |
| 2474 | MZR | RN | Monzonitic-rock | Monzonitic rock | C | DJLO | 18-MAY-06 | TMCM | 31-AUG-18 | I | U |
| 2475 | MZSYS | RN | Sodalite-monzosyenite - A foid-monzosyenite in which the dominant feldspathoid mineral is sodalite. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/06, section 5.1 and fig. 9. | Sodalite-monzosyenite | C | AWEL | 17-DEC-04 | TMCM | 22-FEB-19 | I | R |
| 2476 | NACBT | RN | Natrocarbonatite - A type of carbonatite. In the Rock Classification Scheme, this term may be used when a modal classification is possible. A natrocarbonatite is composed essentially of sodium, potassium and calcium carbonate minerals. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/06, section 6.1 and fig. 25. | Natrocarbonatite | C | GRBA | 24-FEB-00 | TMCM | 22-FEB-19 | R | |
| 2477 | NAMG | RN | Na carbonate sedimentary rock - In the Rock Classification Scheme, these are carbonate sedimentary rocks in which the dominant carbonate mineral is sodium carbonate. The Na carbonate sedimentary rocks are primary precipitates and do not have an unlithified equivalent. They are classified as gaylussite, natron, thermonatrite and trona. British Geological Survey Research Report RR/99/03, section 3.3. | Na carbonate sedimentary rock | C | AWEL | 08-JUN-01 | TMCM | 08-MAR-19 | A |

 Displaying rows 2458 to 2477 of 3677
Displaying rows 2458 to 2477 of 3677



