Vocabularies — view dictionary terms
DIC_META_GLOSSARY (125 rows)
Dictionary table of terms available to applications as Glossary Entries. This is designed for use within the Technical Metadata application but could be adopted for use in other applications.

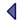 Displaying rows 6 to 25 of 125
Displaying rows 6 to 25 of 125


| Row | CODE | GLOSS_CAT_CODE | TRANSLATION | DESCRIPTION | DATE_ENTERED | DATE_UPDATED | STATUS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | META_DBAMN | METADATA | DATABASE ADMINISTRATOR | The person(s) responsible for managing the physical implementation of the database management system (dbms) on the available computer(s). Includes setting up user ids, allocating space on the computer disks, running backup and recovery procedures. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 7 | META_APMAN | METADATA | APPLICATIONS MANAGER | A skilled SQL-programmer who maintains the structure of the database tables, and provides database application programs, usually for the Data Administrator. (A sub-division of the previous general category `data manager`). | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 8 | META_DATAM | METADATA | DATA MODEL | A representation of the information required by an organisation to function. It can include both digital and non-digital information. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 9 | META_DATAS | METADATA | DATA STANDARD | A standard to which the formal definitions of a data item must conform. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 10 | META_DBANK | METADATA | DATABANK | A BGS definition; a discrete aggregate of Oracle tables which collectively comprise a meaningful data set (ie Borehole data). This is a naming standard to impose meaning on what would otherwise be a large quantity of undifferentiated tables, and to assist in the allocation of management resources to that data. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 11 | META_DB | METADATA | DATABASE | Structured set of data most usually held in a computer, but can be any organised, discrete collection of data. A Database may contain several Databanks, which may contain several Tables. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 12 | META_DSET | METADATA | DATASET | A dataset is best considered as a collection or convenient grouping of data, or individual observations, so that the summary of the information will not be too misleading to others. The data has often been compiled for a specific business purpose or reused for a purpose not origionally envisaged. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 13 | META_DEMTA | METADATA | DETAILED METADATA | This is detailed information about the data themselves. It can be used to describe individual row (or records) or part of a row as well as a dataset itself. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 14 | META_DYMTA | METADATA | DISCOVERY METADATA | The minimum amount of information that is needed to describe a dataset so that a user can determine whether the data in the dataset will be of use to them. It is high-level, generalised information. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 15 | META_DOMA | METADATA | DOMAIN | Strictly, an area of activity or control. This area may define by value the permissible variation for a given data item. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 16 | META_ENTTY | METADATA | ENTITY | A distinct thing, or data object that identifies something of significance. An entity will be defined by possessing one or more attributes. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 17 | META_FORKY | METADATA | FOREIGN KEY | A key which is identical to (and crucially dependent on) a primary key in another table, such as to enable the implementation of a one-to-many join between the two tables. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 18 | META_INDEX | METADATA | INDEX | A cross-referencing mechanism for one or more fields in a database, usually a database table. It can be used to provide faster access to specified data, as well as being used to control uniqueness. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 19 | META_INFO | METADATA | INFORMATION | The meaning derived from data through analysis, or the imposition of structure onto that data; a collected body of knowledge; data organised for purposeful use. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 20 | META_INSTN | METADATA | INSTANCE | In dbms terms, it is the existence of a working copy of Oracle. The Oracle copies on KWDB and MHDB are each an `instances?. It is possible to have two or more instances of Oracle on one machine, each functioning entirely independently of the other. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 21 | META_KEY | METADATA | KEY | A data element (made up of one or more attributes) whose unique value can be used to locate data. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 22 | META_MDATA | METADATA | METADATA | Metadata is information that should allow a Data Manager to describe a dataset so that a user can determine whether the data in the dataset will be of use to them. In the area of Geospatial information this usually means the What, Where, When, How and Who of the data. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 23 | META_NORML | METADATA | NORMALISATION | The analytical process whereby attributes are drawn from an undifferentiated pool of data into discrete sets, or tables, such as to remove duplicate instances of the data, resolve ambiguities, and define primary and foreign key relationships. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 24 | META_PRIKY | METADATA | PRIMARY KEY | A unique identifier for each row in a database table. It is mandatory in a relational database system. This identifier may be comprised of one or more attributes. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |
| 25 | META_TABLE | METADATA | TABLE | A group of records, the equivalent of a flat file. A relational database consists of many tables, each defined by a primary key, and linked to other tables through foreign keys. Table are derived from a heterogeneous collection of data by applying normalisation procedures to that data. | 06-OCT-05 | 10-FEB-06 | C |

 Displaying rows 6 to 25 of 125
Displaying rows 6 to 25 of 125



